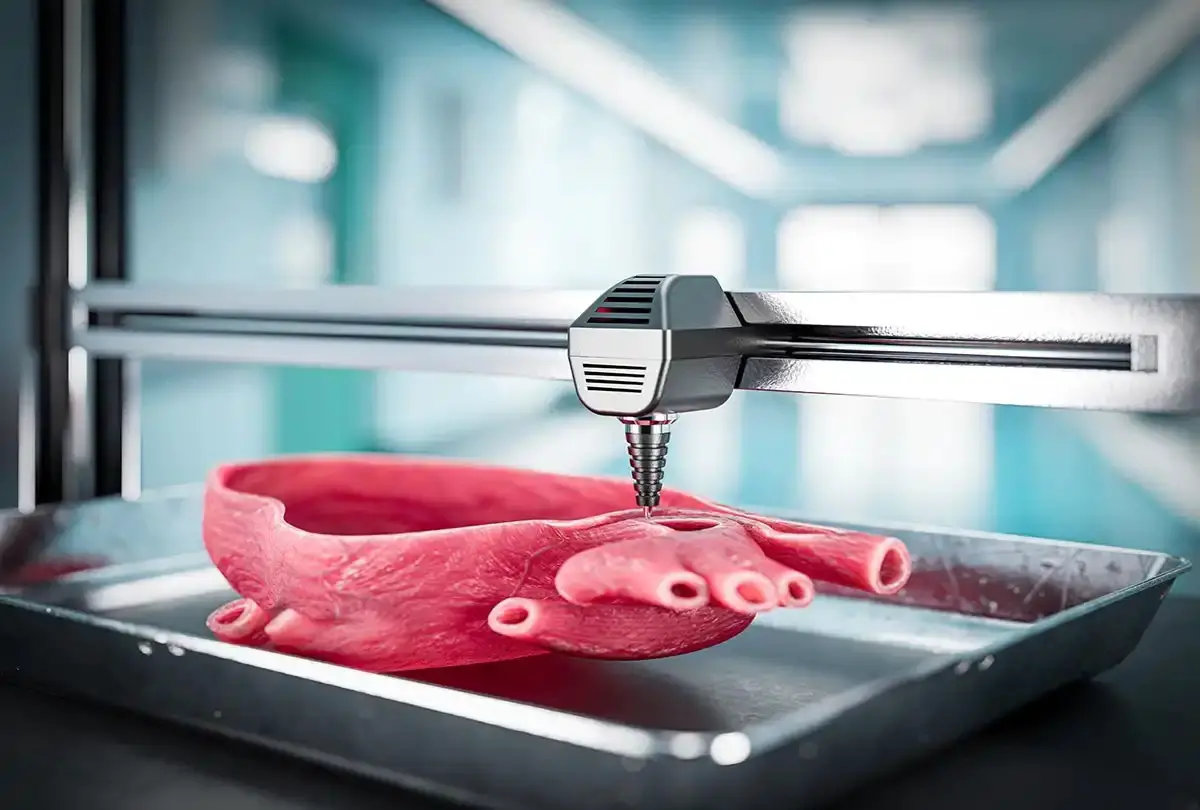
In 2025, The 3D bioprinting future of medicine stands as one of the most transformative breakthroughs in medical technology. No longer a distant dream, bioprinting is enabling scientists and doctors to print living tissues, organs, and custom implants—redefining how we approach transplants, drug testing, and regenerative medicine.
What Is 3D Bioprinting?
3D bioprinting is a specialized form of additive manufacturing that uses bio-inks made of living cells and biomaterials to create structures that mimic natural tissue. These bioprinters layer cells in precise patterns, resulting in tissue that can eventually function like its natural counterpart.
Applications of 3D Bioprinting in Medicine
In 2025, the medical applications of 3D bioprinting are both vast and revolutionary:
1. Organ and Tissue Printing
Scientists are making strides in printing kidneys, livers, and even heart tissues. While full organ transplantation is still being refined, printed tissues are already used for grafts and reconstructive surgeries.
2. Personalized Implants
Bioprinting allows doctors to create custom prosthetics, dental implants, and bone scaffolds tailored exactly to a patient’s anatomy.
3. Drug Testing & Development
Pharmaceutical companies use printed human tissue models to test new drugs, reducing animal testing and increasing reliability.

How 3D Bioprinting Works
The 3D bioprinting process typically involves these key steps:
- Creating a digital blueprint using medical imaging data.
- Formulating bio-ink from stem cells and hydrogels.
- Layer-by-layer printing using a specialized bioprinter.
- Maturation in bioreactors, where the printed structure develops into functional tissue.
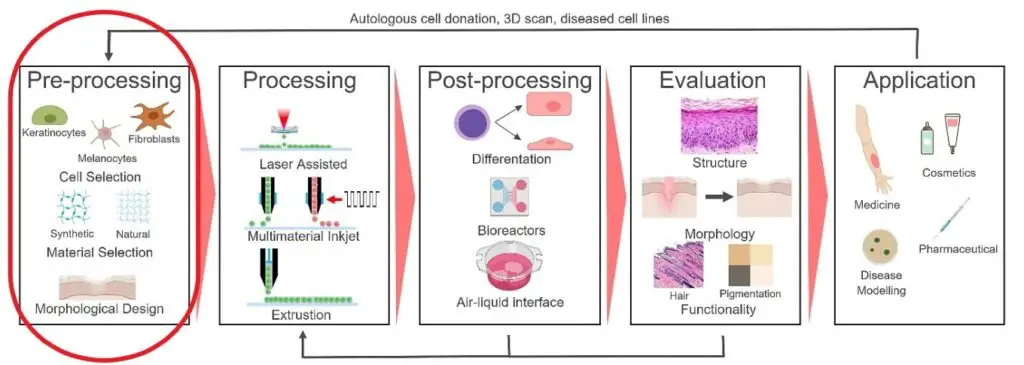
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the promise is huge, challenges remain:
- Ensuring vascularization so that large printed tissues can receive nutrients.
- Ethical questions around human enhancement and cloning.
- Regulatory approval and long-term safety testing.
Still, with rapid progress and global investment, the future of 3D bioprinting in medicine is looking increasingly real.
The Future of Medicine with 3D Bioprinting
By 2030, experts predict we could see:
- Fully transplantable printed organs.
- Bioprinted skin grafts for burn victims.
- In-office bioprinters for rapid tissue repair.
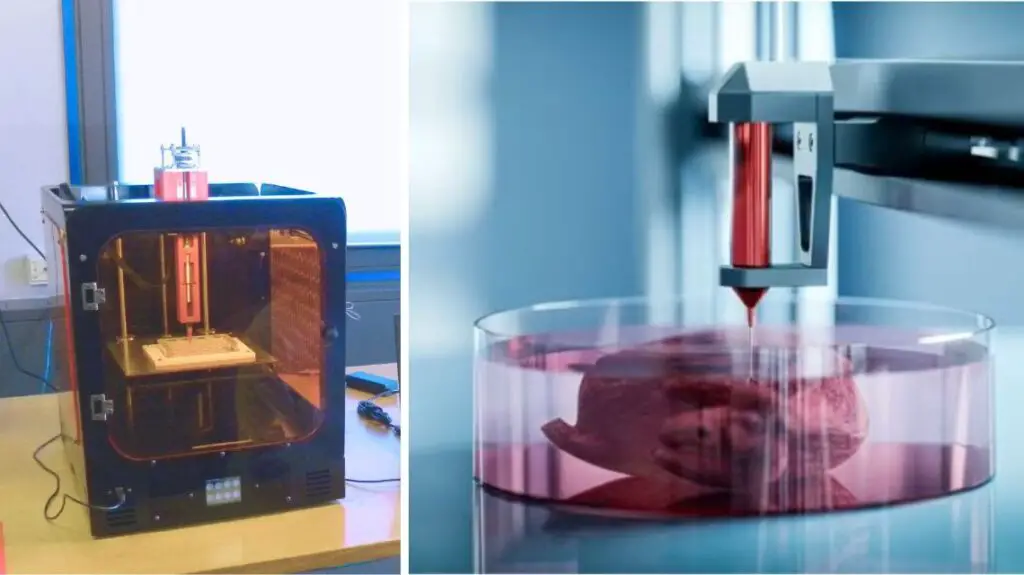

Conclusion: A New Era in Healthcare
3D bioprinting is no longer science fiction—it’s shaping the future of medicine. From personalized care to potential organ replacement, this revolutionary technology is changing how we heal and save lives. As innovation continues, we’re stepping into a future where printed tissue could be just as common as a prescription.
Want to chat? Contact us HERE!